Disabling integrated graphics on your computer is a simple process. Shut down your computer, Open your computer case, Insert the dedicated graphics card, Start your computer and enter the BIOS by pressing the designated key (usually Del, F2, or F10) during startup, Navigate to the Advanced Settings, Select the option to disable, and Install the latest graphics card driver.
Are you looking to upgrade your computer’s graphics card but need to disable the integrated graphics?
Look no further! In this tutorial, we’ll guide you through turning off the iGPU so that you can use a dedicated graphics card for better gaming and video editing performance. By the end of this article, you’ll be able to disable your integrated graphics and enjoy a smoother computing experience.
Also, Read
- Do Motherboards Have Integrated Graphics?
- What Is A Discrete Graphics Card? How Is It Different From An Integrated Graphics Card?
- How to Make Sure a Game Use The Right GPU? Dedicated or Integrated Graphics Card For Windows
What Will You Need To Follow in The Tutorial: How To Disable Your Integrated Graphics?
To disable integrated graphics, you will need the following:
- A PC with an integrated graphics card
- A dedicated graphics card
- The latest graphics card driver
- Basic computer skills
There are a few alternative solutions to disabling integrated graphics, including:
- Disabling iGPU in BIOS
- Using Device Manager to disable GPU
- The author recommends disabling integrated graphics through the BIOS because it provides better control and stability.
Step-by-Step Instructions: How To Disable Your Integrated Graphics?
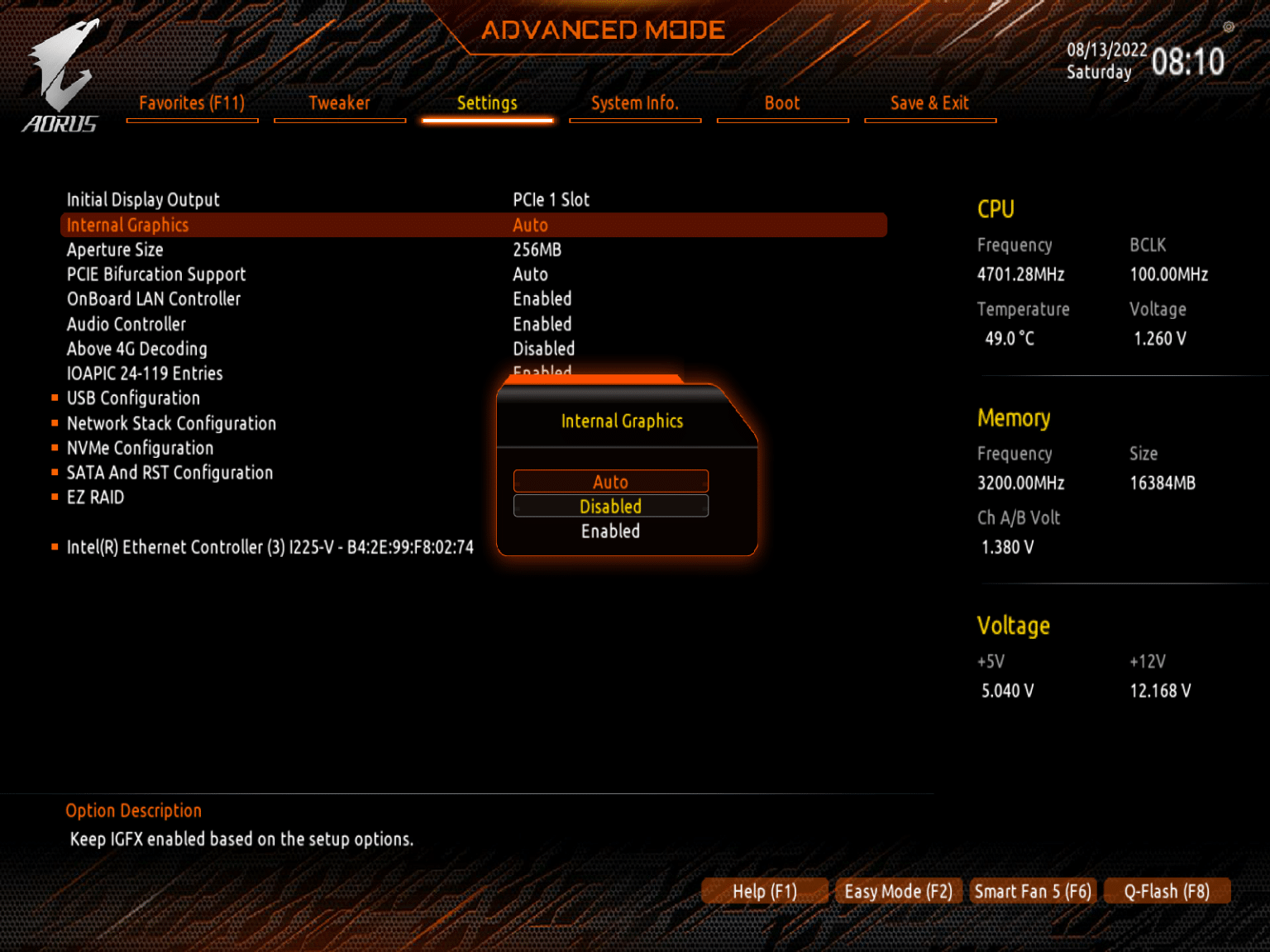
- Shut down your computer and unplug it from the power source.
- Open your computer case and locate the integrated graphics card.
- Insert the dedicated graphics card into an available PCIe slot on the motherboard.
- Connect the monitor to the dedicated graphics card using a compatible cable.
- Start your computer and enter the BIOS by pressing the designated key (usually Del, F2, or F10) during startup.
- Navigate to the Advanced Settings or Integrated Peripherals section and look for an option related to the integrated graphics.
- Select the option to disable the integrated graphics and save the changes.
- Exit the BIOS and restart your computer.
- Install the latest graphics card driver for optimal performance.
The Benefits of Disabling Your iGPU
Disabling your integrated graphics processing unit (iGPU) can offer a few benefits depending on your specific use case. Here are a few potential advantages:
- Improved gaming performance: If you have a dedicated graphics card (GPU) installed in your computer, disabling the iGPU can free up system resources and improve your gaming performance. By default, your computer may use the iGPU for less demanding tasks like web browsing and word processing. By disabling the iGPU, you can ensure that your dedicated GPU is used for gaming instead.
- Better power management: Disabling the iGPU can also improve your computer’s power management. The iGPU consumes a certain amount of power even when not in use, so disabling it can reduce your overall power consumption and extend your battery life if you’re using a laptop.
- Reduced heat output: With the iGPU disabled, one less component generates heat inside your computer. This can help keep your system cooler, leading to improved performance and a longer lifespan for your other components.
- More stable system: In some cases, having both an iGPU and a dedicated GPU can cause stability issues, especially if there are conflicts between the two. Disabling the iGPU can eliminate these potential issues and help ensure your system runs smoothly.
Of course, there are also potential downsides to disabling your iGPU. If you have a dedicated GPU, you’ll retain your computer’s ability to display graphics with one.
Additionally, disabling the iGPU can sometimes cause compatibility issues with specific software programs. Before making any changes to your computer’s configuration, it’s always a good idea to research and ensure you fully understand the potential risks and benefits.
Also, Read
- Are Founders Edition GPUs Any Good?
- What Is Shared GPU Memory? [Everything You Need to Know]
- What Is “Rendering” in Digital Art? [2D/3D]
Justifications for keeping IG enabled
You should keep your integrated graphics processing unit (iGPU) enabled for several reasons, even if your computer has a dedicated graphics card (GPUs) installed. Here are a few potential advantages:
- Power efficiency: The iGPU is designed to be power-efficient, and it consumes far less power than a dedicated GPU. Enrolling the iGPU can extend your battery life and reduce your overall power consumption using a laptop or other mobile device.
- Dual display support: Some computers can simultaneously support multiple displays using the iGPU and dedicated GPU. This can be useful if you need to connect multiple monitors to your system or if you want to use one display for gaming and another for non-gaming tasks.
- QuickSync video encoding: Many modern CPUs have a built-in video encoding feature called QuickSync, which can accelerate video encoding tasks. QuickSync relies on the iGPU, so you may lose this feature if you disable it.
- Troubleshooting: Sometimes, you may encounter issues with your dedicated GPU, such as driver conflicts or hardware failures. In these situations, enabling the iGPU can provide a fallback option for displaying graphics on your system.
- Lower cost: If you’re building a budget system or upgrading an older one, using the iGPU can be a cost-effective option. You won’t have to spend money on a dedicated GPU, and you’ll still be able to handle basic graphics tasks.
Which central processing units (CPUs) have the finest built-in graphics?
There are several CPUs with integrated graphics that offer good performance and value. Here are some of the best options:
- AMD Ryzen 5 5600G: This powerful CPU with integrated Radeon graphics can handle most modern games at 1080p resolution. It has six cores and 12 threads, and its integrated graphics are based on the latest RDNA2 architecture.
- Intel Core i5-11400: This mid-range CPU with integrated Intel UHD 750 graphics that can handle basic gaming and graphics tasks. It has six cores and 12 threads, and its clock speed can reach up to 4.4 GHz.
- AMD Ryzen 7 5700G: This high-end CPU with integrated Radeon graphics can handle demanding games and graphics tasks. It has eight cores and 16 threads, and its integrated graphics are based on the latest RDNA2 architecture.
- Intel Core i7-11700: This high-end CPU with integrated Intel UHD 750 graphics can handle demanding graphics tasks. It has eight cores and 16 threads, and its clock speed can reach 4.9 GHz.
- AMD Ryzen 3 3200G: This budget CPU with integrated Radeon graphics that can handle basic gaming and graphics tasks. It has four cores and four threads, and its integrated graphics are based on the older Vega architecture.
These are just a few of the best CPUs with integrated graphics on the market. When choosing a CPU, you must consider your needs, budget, and factors such as clock speed, core count, and power consumption.
Conclusion
Congratulations, you have disabled your integrated graphics and installed a dedicated graphics card! We hope this tutorial has been helpful and has improved your computing experience.
Remember to comment below and share this article with your friends if you found it helpful. If you’re looking for more ways to improve your computer’s performance, check out our premium offer for expert tips and tricks.
