The ideal temperature range for a GPU is generally between 60- 85 degrees Celsius (140-176 degrees Fahrenheit).
As technology advances and gaming becomes more demanding, the need for high-performance graphics cards increases. However, with high performance come higher temperatures, and it’s important to know what temperature is considered safe for your GPU.
This article will discuss the safe temperature range for different GPUs and tips on keeping your graphics card cool.
Causes GPUs to Overheat

If you constantly power up your electronics, they’ll start to overheat.
In a GPU, the bulk of the heat is produced by the electrical resistance of the components (primarily capacitors and transistors) since energy transfers are never entirely efficient due to the laws of thermodynamics.
Most of the power provided by the PSU is wasted as heat; hence efficiency is measured as a percentage of the intended output (the GPU’s output signal or computations) to the needed input (the watts).
Relating Reading
- How To Overclock Gpu With Evga Precision X?
- How Hot is too Hot for Gaming GPU? Good GPU Temperature Range
- How To Check The CPU And GPU Temperature In Windows 11 Or 10?
- How To Control GPU Temperature? Monitor your Graphic Card Temperature
Safe Temperature Range for GPUs
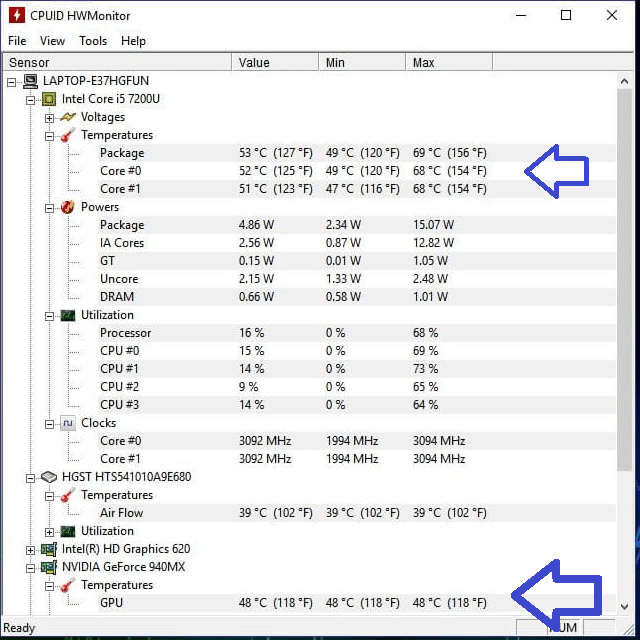
The safe temperature range for GPUs varies depending on the make and model of the graphics card. Generally, the safe temperature range for most GPUs is between 60°C and 85°C.
However, some high-performance GPUs, such as the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090, can operate at maximum temperature up to 90°C without any issues.
It’s important to note that the temperature range provided is just a general guideline and may vary depending on your specific graphics card. You can check the manufacturer’s website or consult the user manual to find the safe temperature range for your specific GPU.
Signs of Overheating GPU
There are several signs that your GPU may be overheating, which include the following:
- Reduced performance: If your GPU is overheating, it may not be able to perform at its maximum capabilities, leading to reduced performance in games or other applications.
- Artifacts on the screen: Overheating can cause visual artifacts, such as lines or static, to appear on the screen.
- Random crashes or freezes: Overheating can cause your computer to crash or freeze unexpectedly.
- Blue screen of death (BSOD): Overheating can cause a BSOD, a severe error requiring you to restart your computer.
- Unusual noise: GPUs with fans can make unusual noise when overheating.
- Temperature reading: You can check the temperature of your GPU using software such as GPU-Z, MSI Afterburner, or EVGA Precision X1. If the temperature is above the safe range for your specific GPU, it may be overheating.
Suppose you notice these symptoms; it’s important to cool down your GPU immediately. This includes taking steps such as cleaning the thermal paste, using a cooling pad or fan, or underclocking or undervolting your GPU.
If the problem persists, you may need to consult the manufacturer for further advice or consider replacing the thermal solution.
Also, Reading
- How to Safely Overclock Your NVIDIA Geforce GTX 1080 Ti Graphics Card – All in One Overclocking Guide!
- How To Overclock GTX 760 Settings With MSI Afterburner?
- How to Overclock AMD Radeon R9 380?
How to Keep Your GPU Cool
Keeping your GPU cool is essential for maintaining its performance and lifespan. Here are some ways to help keep your GPU cool:
- Keep your computer in a well-ventilated area: Good airflow is important for keeping your GPU cool. Ensure your computer is in a room with good airflow, away from any heat sources.
- Dust out your computer regularly: Dust can accumulate in your computer and block airflow, causing your GPU to overheat. Use a can of compressed air to blow out any dust from your computer’s case and the fans on your GPU.
- Use a GPU cooling solution: A cooling pad or fan can help dissipate heat away from your GPU. Make sure the cooling solution you choose is compatible with your GPU model.online pharmacy order valtrex online with best prices today in the USA
- Underclock or undervolt your GPU: Reducing the clock speed or voltage of your GPU can help lower its temperature. However, this will also reduce the performance of your GPU.
- Ensure that your computer’s case has proper airflow: Make sure your computer case has enough space for air to flow through and that the fans are working correctly.
- Clean the thermal paste: Over time, it can dry out, making it less effective at transferring heat away from your GPU. Clean the thermal paste and reapply it to improve the heat transfer.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your GPU will perform at its best and last for a long time.
If you still have issues with your GPU overheating, you may need to consult the manufacturer for further advice or consider replacing the thermal solution.
Different Methods Are Utilized To Cool GPU.
Several methods can be used to cool a GPU, including:
- Air cooling
This method uses fans to dissipate heat away from the GPU. This is the most common method of cooling a GPU and is often built into the GPU itself. Air cooling is relatively simple to set up and maintain and is usually the least expensive option.
- Liquid cooling
This method uses a liquid, such as water or a specialized fluid, to transfer heat from the GPU. This method is more effective than air cooling but can be more complex to set up and maintain. Liquid cooling requires a radiator, pump, and tubing to circulate the coolant and can be more expensive than air cooling.
- Phase-change cooling
This method uses a refrigerant to cool the GPU, similar to how a refrigerator keeps food cool. This method is highly effective but more complex and expensive than other cooling methods.
Phase-change cooling requires a compressor, condenser, and evaporator to circulate the refrigerant.
- Hybrid cooling
Combines air and liquid cooling to provide the best of both worlds. A liquid cooling block is placed on the GPU to dissipate heat, while fans provide additional airflow to keep the GPU cool.
This method provides better cooling than air cooling alone but is more expensive than air cooling.
- Passive cooling
This method does not use fans or pumps to dissipate heat. Instead, it relies on a large heatsink attached to the GPU to dissipate the heat into the air. Passive cooling can be an effective method, but it can be less effective than active cooling methods.
- Overclocking
This method increases the clock speed of the GPU to improve its performance, but it also generates more heat. If overclocking is done carefully, it can prevent the GPU from overheating. Overclocking can be done by software or BIOS settings, but it can void the warranty of the GPU.
The best cooling method for your GPU will depend on your specific needs and budget. For most people, air cooling will be sufficient, but liquid or phase-change cooling may be worth considering if you want the best possible performance.
Factors Impact Your GPU’s Thermals
Several factors can impact the thermals of a GPU temp, including:
- Ambient temperature: The surrounding air’s temperature can affect the GPU’s temperature. If the room or case where the GPU is located is hot, the GPU will also be hot.
- Cooling system: The effectiveness of the GPU’s cooling system, such as the number and size of fans or the type of liquid cooling system, can impact the GPU’s thermals.
- Overclocking: Increasing the clock speed of the GPU can generate more heat and impact the GPU’s thermals.
- Power consumption: The amount of power the GPU consumes can affect the temperature. A GPU consuming more power will generate more heat.
- GPU utilization: The workload of the GPU can affect its temperature. A GPU running at full capacity will generate more heat than one idle.
- Case airflow: The airflow in the case where the GPU is located can impact the GPU’s thermals. Good airflow can help to dissipate heat from the GPU.
- Dust accumulation: If the GPU’s cooling system is clogged with dust, it can impede the ability of the cooling system to dissipate heat from the GPU.
- Quality of thermal paste: The quality of the thermal paste used in the GPU can affect the thermal conductivity between the GPU and the heatsink. A poor-quality thermal paste can lead to a higher GPU temperature.
By understanding these factors, you can take steps to improve the thermals of your GPU, such as improving case airflow, cleaning the GPU’s cooling system, or using a higher-quality thermal paste.
Checking the GPU Temperature
There are several ways to check the temperature of your GPU, including:
- GPU manufacturer software: Many GPU manufacturers, such as Nvidia and AMD, provide software that can monitor the GPU’s temperature. These programs often provide detailed information about the GPU, including the temperature, clock speed, and fan speed.
- Third-party software: Many third-party programs can be used to monitor the temperature of the GPU, such as MSI Afterburner, GPU-Z, and Speccy. These programs are often free and provide detailed information about the GPU, including the temperature, clock speed, and fan speed.
- BIOS/UEFI: Some motherboards have a built-in utility to monitor temperature, voltage, and fan speed; this can be accessed by pressing a specific key during startup, such as Del, F2, Esc, etc.
- Operating system: Some operating systems, such as Windows, have built-in tools that can be used to monitor the temperature of the GPU. For example, in Windows, you can open the Task Manager, go to the Performance tab, and see the GPU temperature under the “GPU” section.
- Hardware monitoring: Some high-end motherboards or other devices have built-in sensors that can monitor the GPU temperature; you can use the device’s software to monitor the temperature.
It’s important to note that the temperature readings can vary depending on the method used to check it, so it’s best to use a consistent method to ensure accurate temperature monitoring over time.
It’s also important to note that different GPUs have different ideal temperature ranges, typically between 60-85 degrees Celsius. Hence, it’s essential to refer to the GPU’s documentation or the manufacturer’s website for the recommended temperature range for your specific GPU.
If Your GPU Overheats, then What Happens?
When a GPU gets too hot, it can cause several problems, including:
- Thermal throttling: When the GPU gets too hot, it will reduce its clock speed to reduce heat output. This can cause the GPU to perform more slowly and lead to lower frame rates in games or slow rendering times in applications that use the GPU.
- System crashes: If the GPU gets too hot, it can cause the system to crash or freeze. This can be caused by several factors, including overheating of the GPU, overheating of other components, or a lack of power to the GPU.buy hydroxychloroquine online https://bioage.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/png/hydroxychloroquine.html no prescription pharmacy
- Damage to the GPU: If the GPU gets too hot, it can cause damage to the GPU itself. This can include damage to the transistors or other components of the GPU, which can lead to a loss of performance or even permanent damage to the GPU.
- Shortening the lifespan of the GPU: Overheating can also cause wear and tear on the GPU over time, which can shorten its lifespan.
- Reduced overclocking headroom: Overheating can also cause the GPU to thermal throttle at lower clock speeds, reducing the amount of overclocking headroom available.
It’s essential to take steps to prevent your GPU from getting too hot, such as ensuring proper cooling and airflow, monitoring the GPU’s temperature, and taking action if the GPU starts to get too hot.
Regularly cleaning the GPU’s cooling system, using a better thermal paste, and checking the airflow in the case can also help prevent your GPU from getting too hot.
If you are overclocking, monitoring the GPU’s temperature more closely is essential, as overclocking can cause the GPU to run hotter than usual.
Conclusion
Keeping your GPU at a safe temperature is essential for maintaining its performance and lifespan. By understanding the safe temperature range for your specific GPU and being aware of the signs of overheating, you can take the necessary steps to keep your graphics card cool.
Remember to keep your computer in a well-ventilated area, dust out your computer regularly, use a GPU cooling solution, underclock or undervolt your GPU, and ensure that your computer’s case has proper airflow.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your GPU will perform at its best and last for a long time.
Frequently Asked Question
What temperature is considered too hot for a GPU?
The ideal temperature range for a GPU varies depending on the specific GPU model and manufacturer. However, most GPUs are generally designed to operate within a temperature range of 60-85 degrees Celsius (140-176 degrees Fahrenheit).
It’s essential to refer to the documentation or the manufacturer’s website for the recommended temperature range for your specific GPU. Going beyond the recommended range can lead to thermal throttling and can cause permanent damage to the GPU.
Can a GPU overheat if it’s not under heavy load?
Yes, a GPU can overheat even if it is not under heavy load. Several factors, including poor cooling, a lack of airflow, or a malfunctioning cooling system, can cause this.
What are some signs of an overheating GPU?
Some signs of an overheating GPU include thermal throttling, system crashes, visual artifacts, and system freezes.
How can I prevent my GPU from overheating?
To prevent your GPU from overheating, you can ensure proper cooling and airflow, monitor the GPU’s temperature, and take action if the GPU starts to get too hot.
Regularly cleaning the GPU’s cooling system, using a better thermal paste, and checking the airflow in the case can also help prevent your GPU from getting too hot. If you are overclocking, it is important to monitor the GPU’s temperature more closely, as overclocking can cause the GPU to run hotter than usual.
Can an overheating GPU cause permanent damage?
Yes, an overheating GPU can cause permanent damage to the GPU, including damage to the transistors or other components. It can also shorten the lifespan of the GPU.
Therefore, it is important to prevent your GPU from overheating and to take action if the GPU starts to get too hot.
