How to Undervolt CPU? Download and install ThrottleStop, Open ThrottleStop, click on the “FIVR” button, Check the “Unlock Adjustable Voltage” box, Lower the “Core Voltage Offset” by 50mV, and click “Apply.” Run a stress test like Prime95 or AIDA64 and monitor your CPU’s temperature.
Undervolting the CPU reduces the voltage supplied to the processor, which can lead to decreased power consumption and temperature. To undervolt, a CPU, follow the step-by-step guide below.
How to undervolt a CPU is crucial for anyone looking to improve their computer’s performance while reducing energy consumption. Undervolting is a process that helps optimize your computer’s power usage, leading to lower temperatures and longer battery life.
This tutorial will teach you to undervolt your CPU and perform better without sacrificing stability.
What Will You Need to Follow in the Tutorial: How to Undervolt CPU?
Before you start undervolting your CPU, you will need the following:
- A computer with a CPU that supports undervolting
- A stress testing tool like Prime95 or AIDA64
- A monitoring tool like HWMonitor or ThrottleStop
- A program that allows you to undervolt your CPU, such as Intel XTU or ThrottleStop
Several programs are available for undervolting, but we recommend ThrottleStop for its ease of use and compatibility with most CPUs. ThrottleStop is also free and open-source.
Related Read
- What is CPU Virtualization Technology?
- What Socket Type is Soldered To The Motherboard, Along With The CPU?
- How To Install Windows 11 on an Unsupported CPU?
Step-by-Step Instructions: How to Undervolt CPU?
- Download and install ThrottleStop.
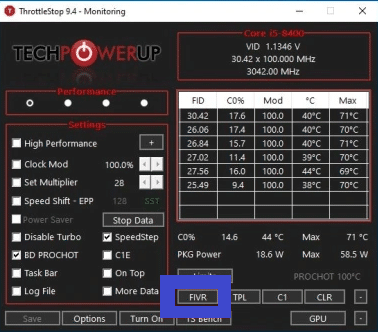
- Open ThrottleStop and click on the “FIVR” button.
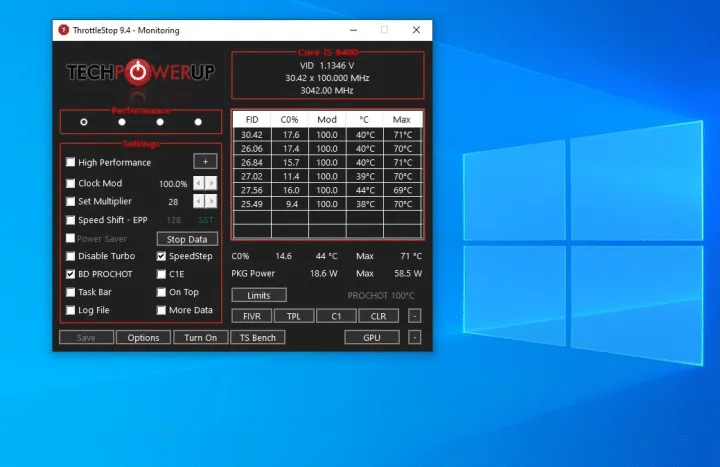
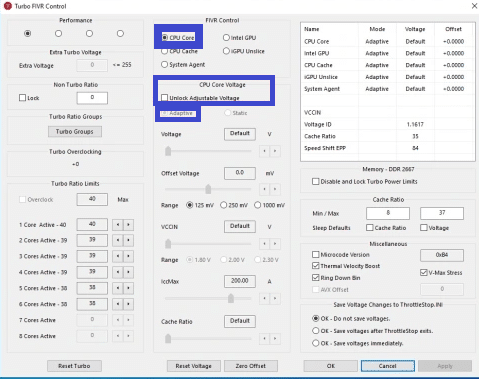
- Check the “Unlock Adjustable Voltage” box.
- Lower the “Core Voltage Offset” by 50mV and click “Apply.”
- Run a stress test like Prime95 or AIDA64 and monitor your CPU’s temperature and stability using HWMonitor or ThrottleStop.
- If the stress test passes, repeat Step 4 and lower the voltage offset by another 50mV. If the test fails, increase the voltage offset by 10mV.
- Repeat Steps 5 and Step 6 until you reach a stable undervolt. Keep in mind that undervolting too much can lead to instability and crashes.
Also, Read
Undervolting vs Underclocking vs. Overclocking
Undervolting, underclocking, and overclocking are all techniques used to manipulate the performance and power consumption of computer components such as the CPU and GPU. Here’s a brief explanation of each:
- Undervolting: This involves lowering the voltage supplied to a component while maintaining the same clock speed. Undervolting can reduce power consumption and heat generation, resulting in longer battery life for laptops and lower cooling requirements for desktops. However, it may also affect stability and performance if done excessively.
- Underclocking: This refers to reducing the clock speed of a component while maintaining the same voltage. Underclocking can reduce power consumption and heat generation but may also reduce performance, particularly in tasks requiring high clock speeds.
- Overclocking: This involves increasing the clock speed of a component beyond its default settings. Overclocking can result in increased performance but also increase power consumption and heat generation. Overclocking can also reduce the lifespan of a component if done excessively or without proper cooling.
These techniques can help fine-tune computer components‘ performance and power consumption. Still, they should be used cautiously and only by experienced users who understand the risks and potential consequences.
Also, Read
- How To Check What CPU I Have?
- What Are The Best Places To Buy PC Parts, CPUs & Graphics Cards Online?
- How To Check Cpu? (And How Fast it is)
Is undervolting the CPU safe?
Undervolting the CPU can be safe if done correctly and in moderation. Lowering the voltage supplied to the CPU can help reduce power consumption and heat generation, which can result in better performance and a longer lifespan of the CPU.
However, undervolting too much or improperly can cause instability, crashes, and potential damage to the CPU. It’s essential to use a reliable software tool designed for undervolting and to test the stability of the CPU after making any changes.
Additionally, undervolting may void the warranty of the CPU, so it’s essential to consider the potential risks and benefits before attempting it.
Prepare CPU for Undervolting
Before undervolting the CPU, it’s essential to prepare it to ensure that the process is as safe and effective as possible. Here are some steps you can take:
- Monitor CPU temperatures: Check the temperatures of your CPU while it’s running under typical loads to get a sense of its baseline performance. This will help you assess the effectiveness of your undervolting efforts.
- Update BIOS and drivers: Ensure that your BIOS and drivers are up to date to ensure compatibility with undervolting software and to avoid potential compatibility issues.
- Stress test CPU: Stress test your CPU to assess its stability under heavy loads. This will help you identify any potential issues with stability after undervolting.
- Determine undervolting limits: Determine the undervolting limits of your CPU by gradually reducing voltage and monitoring performance and stability. This will help you find the sweet spot between performance and power consumption.
- Use reliable undervolting software: Use a reliable software tool designed for undervolting, as this will help ensure that the process is safe and effective. Avoid using unknown or untested software, which can damage your CPU.
By taking these steps, you can prepare your CPU for undervolting and minimize the risk of potential issues while optimizing performance and power consumption.
Also, Read
- How to Remove a CPU Cooler or Fan Without Damaging the Motherboard?
- How to Clean A CPU Fan Of Your Computer System in 5 Simple Steps?
- How To Install A Liquid Cooling System (AIO) On Your CPU?
How to undervolt your CPU with AMD Ryzen Master?
Undervolting your AMD Ryzen CPU using AMD Ryzen Master is relatively simple. Here are the steps:
- Download and install AMD Ryzen Master: First, download and install the AMD Ryzen Master software from the AMD website.
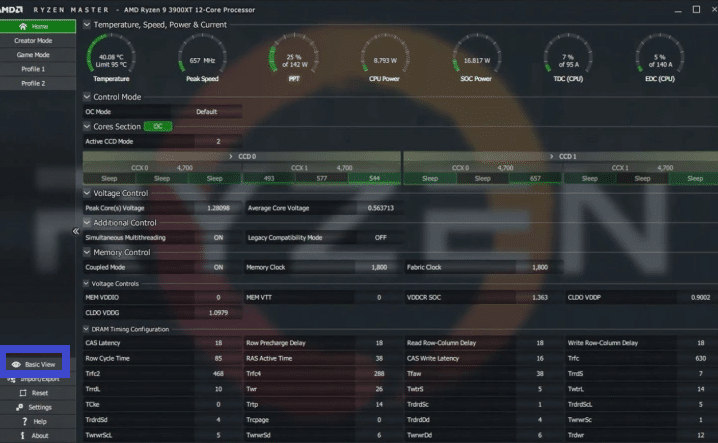
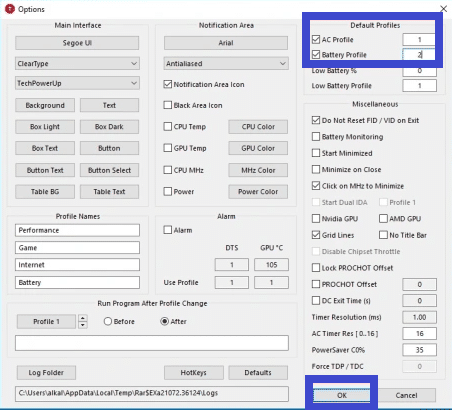
- Open AMD Ryzen Master: Open the software and select the “Profile 1” tab to create a new profile once installed.
- Adjust the voltage: In the “Profile 1″ tab, scroll down to the “Core Voltage” section and adjust the voltage offset by reducing it in small increments (-0.05V, for example). This will reduce the voltage supplied to the CPU and lower power consumption and heat generation.
- Apply the undervolting: After adjusting the voltage offset, click “Apply” to save the changes.
- Test stability: Once the undervolting is applied, stress tests the CPU to ensure stability. You can use a tool like Prime95 or AIDA64 to stress test the CPU and monitor temperatures.
- Adjust further: If the undervolting is stable, you can continue to reduce the voltage offset in small increments until you reach the point where the system becomes unstable.
- Save the profile: Once you’ve found the ideal undervolting settings, save the profile for future use by clicking “Save Profile” and selecting a location to save the file.
Undervolting can potentially void your CPU warranty and should be done cautiously. Additionally, undervolting can affect performance, so it’s essential to test the stability and performance of your CPU before and after undervolting.
Benefits of Undervolting CPU
Undervolting the CPU can provide several benefits:
- Reduced power consumption: Undervolting can reduce the voltage supplied to the CPU, which can reduce power consumption. This is especially beneficial for laptops, as it can increase battery life and reduce the need for frequent charging.
- Lower temperatures: A reduction in voltage can also result in lower temperatures, which can help improve the longevity of the CPU and other components. Additionally, it can help reduce the need for robust cooling solutions, which can be noisy or take up a lot of space in the case.
- Improved stability: Undervolting can help stabilize the CPU, as lower temperatures and power consumption can help reduce the likelihood of crashes and other stability issues.
- Increased overclocking headroom: Undervolting can also provide more headroom for overclocking, as it can help reduce power consumption and heat generation, allowing for higher clock speeds and better performance.
- Environmental benefits: Undervolting can also reduce the environmental impact of computing, as it can reduce power consumption and carbon emissions from power generation.
Overall, undervolting the CPU can provide several benefits, including increased battery life, improved stability, reduced temperatures, and increased overclocking potential. However, it’s important to note that undervolting should be done cautiously and only by experienced users who understand the risks and potential consequences.
Conclusion
Undervolting your CPU is a great way to optimize your computer’s power usage and achieve better performance without sacrificing stability. Following the step-by-step guide above, you can safely and effectively undervolt your CPU.
If you enjoyed this tutorial, please comment below and share it with your friends. Also, remember to check out our premium offer for more advanced tips and tricks on computer optimization.
